| Section | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Who we are | Here, the presenters who developed this Learning and Teaching Package (LTP) introduce themselves. To go to the next page, press the button with a gray background that says Next: |
|
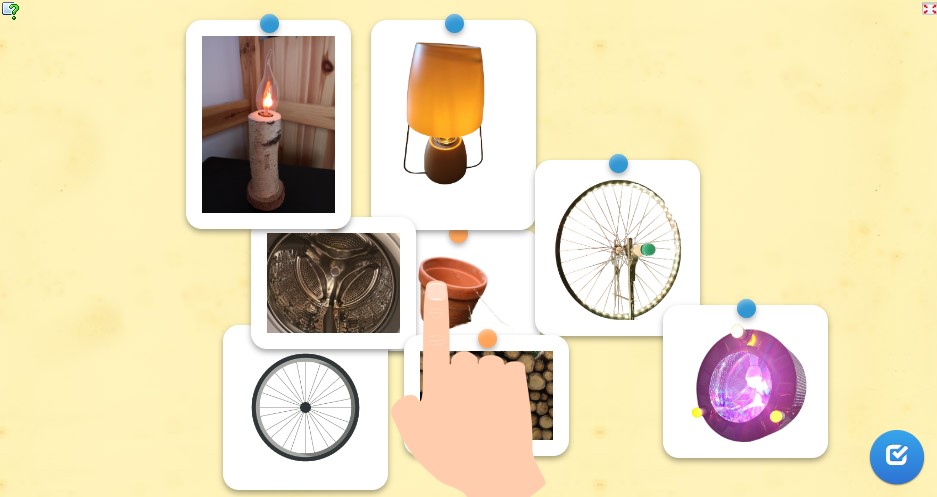
| Unit 1 - Introduction: The relationship between digitality and sustainability |  #01 Tasks: SustainabilityCheck out the Interactive Image: Sustainability.  Write down all key terms and their meanings in the Glossary: Sustainability and Digitality. Write down all key terms and their meanings in the Glossary: Sustainability and Digitality. Take the quiz: Quiz: Sustainablity. Check out the Educational Resources page for more materials on the topic of sustainability, which you are welcome to view. On the Scientific sources page you will find scientific texts that give you even more information on the topic of sustainability. To go to the next page, press the button with a gray background that says Next:  |
|
#02 Tasks: Digitality Write down all key terms and their meanings in the Glossary: Sustainability and Digitality. Write down all key terms and their meanings in the Glossary: Sustainability and Digitality.Take the quiz: Quiz: Digitality. Check out the Educational Resources page for more materials on the topic of digitality, which you are welcome to view. On the Scientific sources page you will find scientific texts that give you even more information on the topic of digitality. To go to the next page, press the button with a gray background that says Next:  |
||
Check out the video:   Write down all key terms and their meanings in the Glossary: Sustainability and digitality. Write down all key terms and their meanings in the Glossary: Sustainability and digitality.Take the quiz: Quiz:  Check out the Educational Resources page for more materials on the topic of the Relationship between digital technology and sustainability, which you are welcome to view. On the Scientific sources page you will find scientific texts that give you even more information on the topic of the Relationship between digital technology and sustainability. To go to the next page, press the button with a gray background that says Next:  |
||
 After viewing the content for Sustainability, Digitality and Relationship between digital technology and sustainability, answer the following questions on the collaborative interactive whiteboard: 1) What was new to me? 2) Where do I still have open questions? 3) Where does the topic have relevance to me and my work or studies? Give one or two examples. We will discuss the results on the ineractive whiteboard in a face to face setting. [The following link refers to an example of an online-pinboard. Please insert a link to an online-pinboard of your own.] |
||
An exciting experiment awaits you here!
|
||
Here you can find the Worksheet: Explore the environment with your smartphone in different formats. Once as a pdf file, so that you can use it directly in class or in teaching. The other file is in .pptx format so that you can modify the worksheet to suit you and your teaching.
The Worksheet: Explore the environment with your smartphone has a CC0 licence, so no rights are reserved. So feel free to modify and adapt the worksheet! Feel free to upload the result of your adjusted worksheet HERE. |
||
With this collaborative Taskcard-pinboard, we can collect apps and the experience of using these programs to explore the world. |
||
Walk through the environment with your eyes open and notice how digital technologies influence and integrate into the environment. |
||
| Unit 2 - My Smartphone, Planet Earth & Me | ||
Life cycle of a smartphone with short quiz |
||
Activity to raise awareness among pupils. |
||
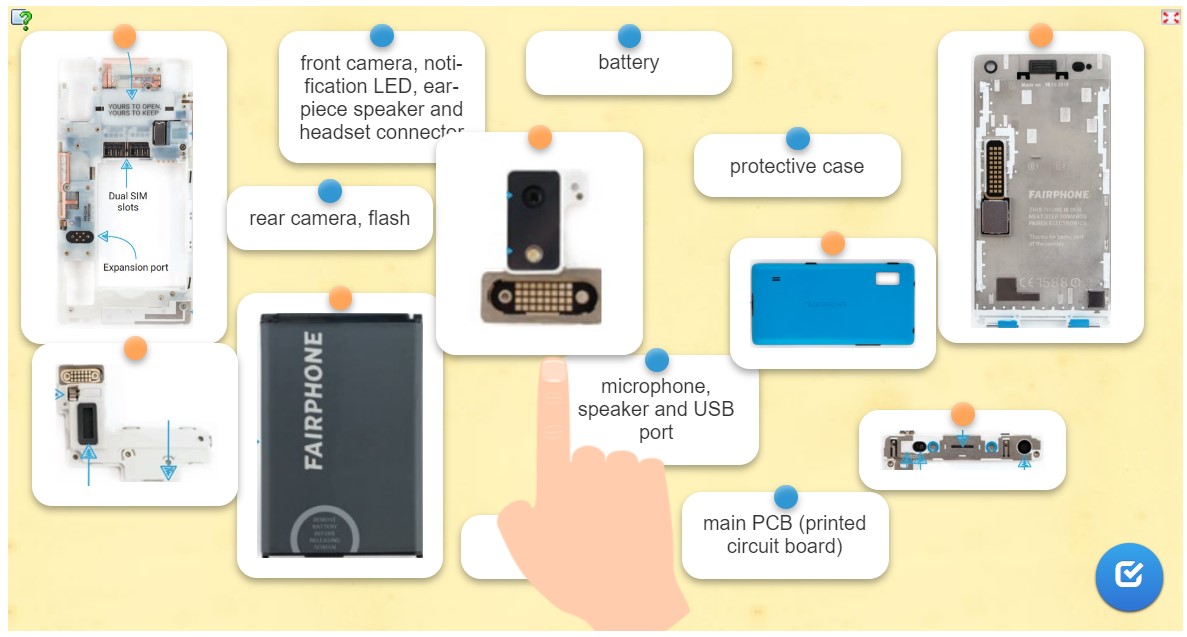
The journey of a conflict-free mineral into the Fairphone 2. |
||
What kinds of valuable rare minerals are in a smartphone? Take a closer look and consider the sustainability of phone production. |
||
|
||
A lot of the things we own seem to inevitably end up in the trash. That's kind of a shame because most of those things can be upcycled in tons of fun and creative ways. This, in turn, reduces waste, which is great for the environment. |
||
Activity to reflect on your own media use, media acquisition and media disposal. Based on these reflections, a discursive exchange of the participants is guided by the teacher. |
||
If you don't have the possibility to disassemble a smartphone yourself there is a video provided here. |
||
| Unit 3 - The digital technology network on the globe | "Energy is critical to our modern lives. But our increasing demand for it has created a range of political, social and environmental problems." (LifeSquared) |
|
"The first rendering displays the relative densities of Internet connectivity across the globe.." (Chris Harrison) |
||
"Worldview Upgrader is a fun educational tool created to help people rid themselves of common systematic misconceptions about global development." (Gapminder) |
||
"Watch everyday life in hundreds of homes on all income levels across the world, to counteract the media’s skewed selection of images of other places." (Gapminder) |
||
The part that artificial intelligence plays in climate change has come under scrutiny, including from tech workers themselves who joined the global climate strike last year. Much can be done by developing tools to quantify the carbon cost of machine learning models and by switching to a sustainable artificial intelligence infrastructure. |
||
This video explains climate change to children. This video is an additional resource to the Start-Up. |
||
The Climate Handprint is the complement to the CO2 Footprint. It shows and measures what we can do to protect the climate. We increase it through our own actions and by supporting social change. This site is in German. |
||
"Ecological Footprint? How many planets do we need if everybody lives like you? When is your personal Overshoot Day" |
||
German climate psychologist Thomas Brudermann provides illustrations related to climate psychology in German and English. These can be used under the Creative Commons licence CC-BY-ND. They may be useful for further discussion. |
||
"About 300 undersea fiber optic cables are responsible for 99% of international data traffic". Isn't it interesting that our "wireless" internet relies on cables that lie deep down in our oceans? |
||
Use worksheet 3 and the website about submarine cables to find out about how computers are connected. To visualize, put threads to show the cables (groupwork). Ask the students to imitate how the cables connect us digitally. You can play a game depicting a signal going from Point A to B. |
||
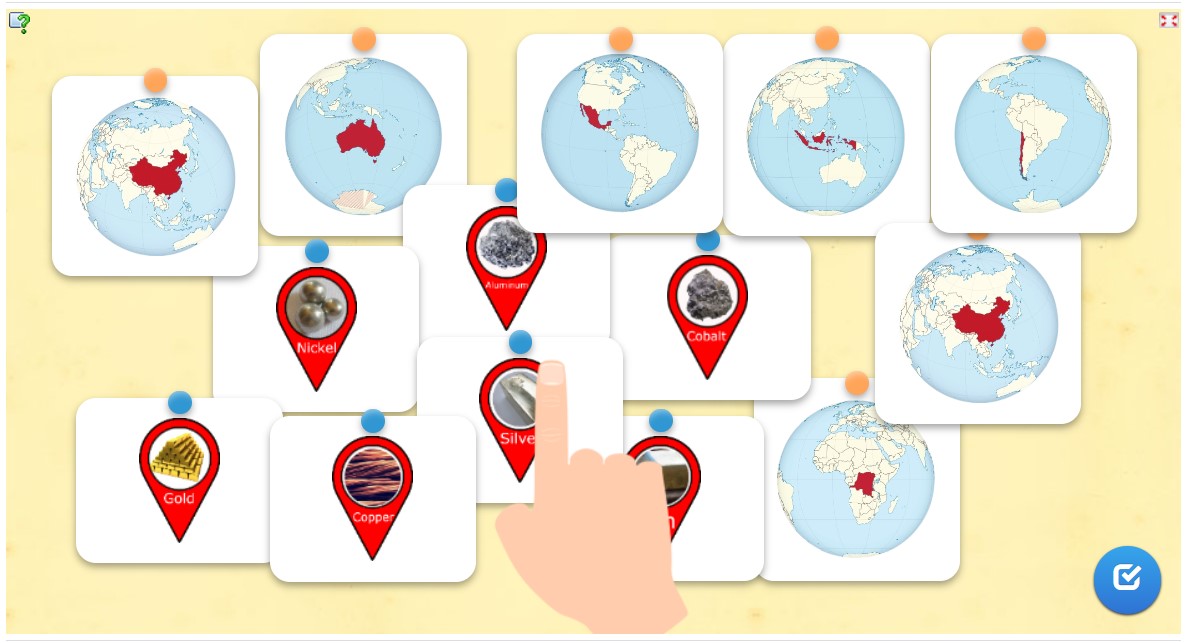
Next use worksheet 4 and this website about data centres to find out major data centres and server farms are located around the world. To visualize, take wooden cubes (groupwork). Ask the students to place them on the countries and continents that have the largest data centres and server farms. |
||
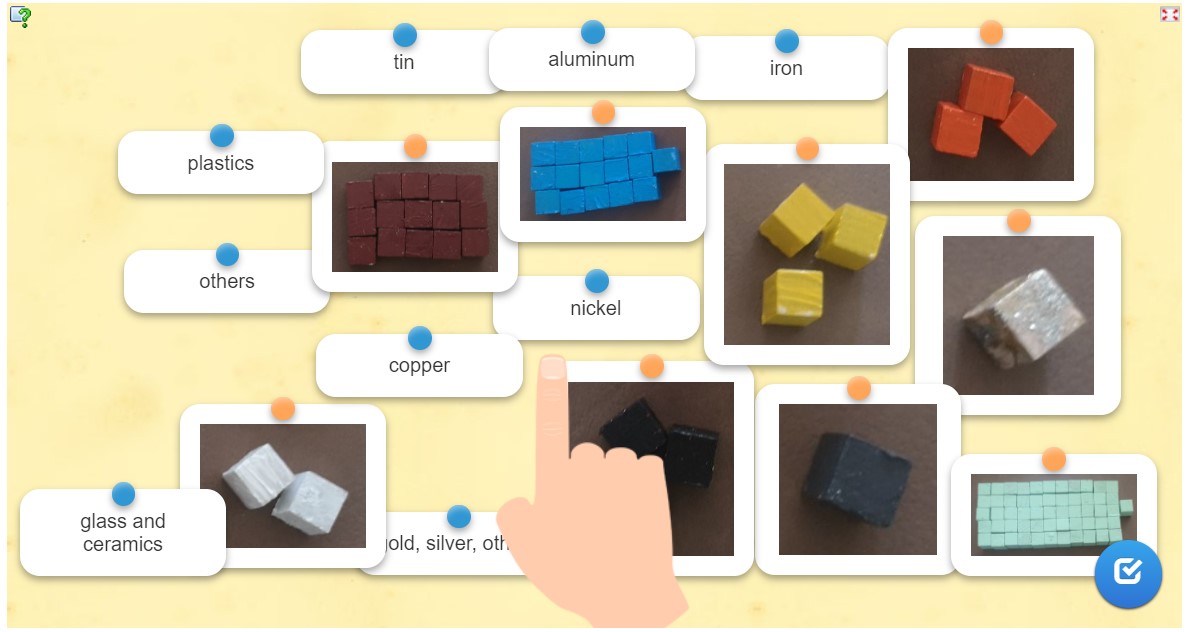
Next use worksheet 5 and the website about e-waste to find out which countries produce a lot of e-waste and which don’t. To visualize, take e-waste samples (groupwork). Ask the students to place them on the countries which produce a lot of e-waste and which don’t. |
||
| Unit 4 - A Future with or without Technology? | ||
You can also collect your demands for your joint resolution in a digital tool here. We use taskcards for this purpose, for example. |
||



 Task:
Task: